
When you look at an object, light from the object passes through the cornea, then the lens and then hits the retina at the back of the eye. Bruch's membrane is a thin protective barrier between the choroid and the delicate retina. The tiny blood vessels of the choroid bring oxygen and nutrients to the retina. The fovea forms your pinpoint central vision. In the middle of the macula is an area called the fovea, which only contains cones. The macula is the most densely packed with rods and cones. The macula is the small area of the retina where your central vision is formed. It acts like a filter, keeping harmful substances away from from the sensitive cells. The RPE helps to nourish and support the rods and cones. The outer layer - the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) - is a layer of cells behind the rods and cones.

The cones help us to see in the daylight, and form colour vision. These cells react to light and send electrical signals via the optic nerve to the brain.

There is an inner layer of 'seeing cells' called rods and cones. The retina is made up of two main layers. For additional information visit Linking to and Using Content from MedlinePlus.د.مصطفى الجزار, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commonsīy د.مصطفى الجزار (Own work) CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited without authorization. Links to other sites are provided for information only - they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. This site complies with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information: verify here. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy editorial process and privacy policy. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability.

is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. The macula is the part of the retina responsible for sharp, detailed vision.Ī.D.A.M., Inc. Central vision becomes severely affected if the macula becomes detached.
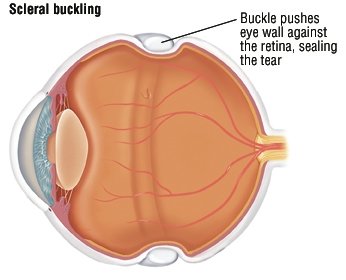
When the retina becomes detached, bleeding from nearby blood vessels can cloud the inside of the eye so that you may not see clearly or at all. This type occurs in people who have uncontrolled diabetes, had retinal surgery before, or have long-term (chronic) inflammation. Another type of retinal detachment is called tractional detachment.A family history of retinal detachment also increases your risk. This is most often caused by a condition called posterior vitreous detachment. It can also be caused by trauma and very bad nearsightedness. This causes the retina to separate from the underlying tissues, much like a bubble under wallpaper. The most common type of retinal detachment is often due to a tear or hole in the retina.Light rays that enter the eye are focused by the cornea and lens into images that are formed on the retina. The retina is the clear tissue that lines the inside of the back of the eye.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
